The spelling debate between “traveler vs traveller” is one that confuses many, especially those who write or travel often. The differences are not merely a matter of personal choice; they are influenced by historical events, regional customs, and even the spread of digital language. In this article, we’ll explore the origins of these two spellings, examine their use across different English-speaking regions, and provide practical tips for when to use each one.
Origins of the Spelling Difference
The distinction between “traveler vs traveller” dates back centuries and is rooted in the evolution of the English language. The word “traveller” was used in Old and Middle English, adhering to the traditional spelling rules of the time. However, in the early 19th century, American lexicographer Noah Webster sought to simplify English spelling, aiming to establish a distinctly American language. As part of this reform, he changed many words, including “traveller,” to the shorter “traveler.” This change made spelling more consistent and easier to learn, especially by removing unnecessary letters like the double “l” in certain words.
In contrast, British English retained its traditional forms. The British preferred the extra “l” in words like “traveller,” “cancelled,” and “modelled,” believing it kept the integrity of older English spelling patterns intact. While Americans embraced Webster’s simplified rules, the British remained loyal to their historical roots. This divergence in spelling preferences has persisted ever since.
Table 1: Origins of “Traveler” vs. “Traveller”
| Spelling | Region | Historical Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Traveler | United States | Influenced by Noah Webster’s reforms |
| Traveller | United Kingdom, Canada, Australia | Retained traditional British spelling |
Regional Preferences: American vs. British Usage
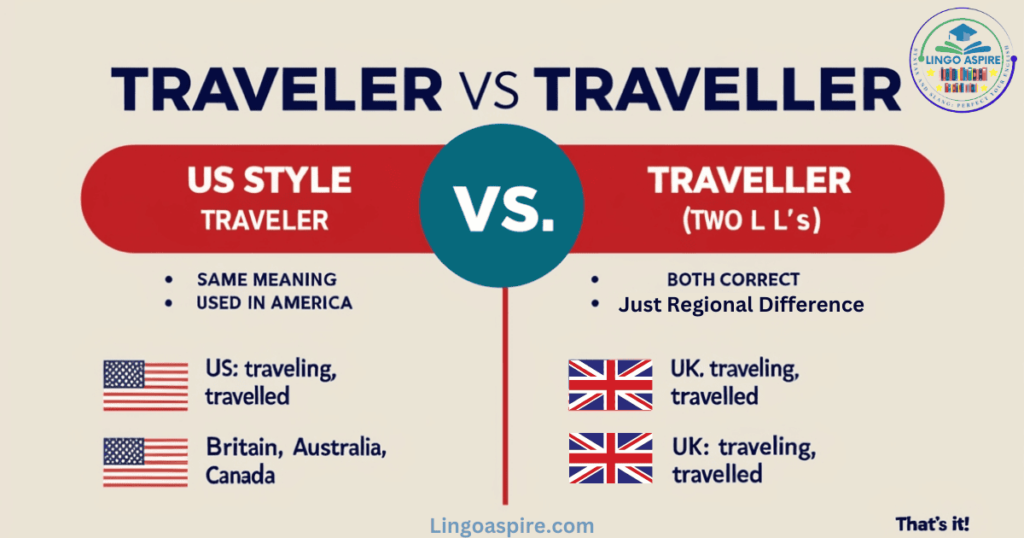
The primary distinction between “traveler” and “traveller” lies in the regional preferences of English speakers. In the United States, “traveler” is the standard form. Since the 19th century, this has been the proper usage in American English, reinforced by educational institutions, government documents, and media. On the other hand, British English prefers “traveller,” and this is the accepted spelling in the UK, Canada, Australia, and other countries that follow British spelling conventions.
This distinction is not limited to the word “traveller” alone. Other English words exhibit a similar pattern, where American English uses the single consonant form, while British English retains the double consonant. For example, “color” versus “colour” or “defense” versus “defence.” These spelling differences are a reflection of the broader differences between American and British English and the historical development of each.
Table 2: American vs. British Usage Examples
| American English | British English |
|---|---|
| Traveler | Traveller |
| Color | Colour |
| Honor | Honour |
| Defense | Defence |
The spelling differences help define the identity of each variety of English and guide writers in choosing the appropriate form based on their audience.
Rules for Correct Usage in Writing
Knowing when to use “traveler” versus “traveller” depends largely on the proper usage for your audience. If you are writing for an American readership, using “traveler” is the natural choice. This aligns with American spelling norms and ensures that your work resonates with your audience. Conversely, if your readers are primarily British, Canadian, or Australian, “traveller” should be used.
In formal contexts, such as academic writing or business communication, it is crucial to remain consistent. Switching between “traveler” and “traveller” within the same document can confuse your readers and appear unprofessional. Most style guides, such as the Oxford English Dictionary, recommend adhering to the spelling conventions of your target audience.
Examples of Correct Usage:
- In American English: “The seasoned traveler knows the best places to visit in the city.”
- In British English: “The dedicated traveller enjoys exploring the lesser-known attractions.”
By aligning your spelling with the audience’s expectations, you maintain professionalism and clarity in your writing.
Evolution of Language and Global Trends
The advent of the internet and global communication has blurred the lines between American and British English. Through social media, blogs, and other digital platforms, people around the world encounter both “traveler” and “traveller” regularly. This exposure has led to a growing acceptance of both spellings in international contexts. While regional spelling preferences still exist, there is now greater flexibility in using either form, especially for global audiences.
Technology and globalization have played a significant role in this shift. With digital content reaching readers from different parts of the world, the pressure to adhere strictly to one form of spelling has decreased. People now expect to see both variations, and many online platforms even automatically correct “traveller” to “traveler” depending on the user’s language setting.
Looking forward, it is likely that both spellings will coexist, with each remaining firmly entrenched in their respective regions. However, as English continues to evolve, we may see a gradual shift toward greater uniformity, especially as English becomes even more widely used as a global lingua franca.
Practical Tips for Writers and Content Creators
For writers and content creators, the key to managing language differences between “traveler” and “traveller” is consistency. If you’re unsure which version to use, follow these practical steps to stay on track:
- Know your audience: If you’re targeting American readers, stick with “traveler.” If you’re writing for British, Canadian, or Australian audiences, use “traveller.”
- Choose a style guide: Follow a specific style guide that matches your region. American writers can refer to the Chicago Manual of Style, while British writers can consult Oxford Style Manual for guidance.
- Use writing tools: Tools like Grammarly or Word’s built-in spell check feature can help you maintain consistent spelling. Set your language preferences to avoid mixing “traveler” and “traveller.”
- Stay consistent: Avoid switching between spellings within the same document. This ensures a smooth reading experience for your audience.
By following these tips, you can easily navigate the spelling debate and focus on creating high-quality content that resonates with your readers.
Conclusion: Does It Really Matter?
In the end, the choice between “traveler vs traveller” boils down to audience preference and regional customs. Both spellings are correct, but understanding the context in which they should be used is essential for clear communication. The proper usage depends on whether your audience follows American or British English conventions.
Rather than getting caught up in rigid rules, it’s important to be adaptable. As language evolves and global communication continues to shape how we interact with one another, we may see these distinctions blur further. For now, it’s best to choose the version that aligns with your target audience, and stick with it consistently throughout your writing.
Sources and Further Reading
- Merriam-Webster Dictionary
- Oxford English Dictionary
- “The Evolution of English Spelling,” Journal of Linguistics
- Style guides: APA, MLA, and Oxford
This guide not only clarifies the spelling debate but also offers practical advice for those navigating the world of English spelling and usage. Whether you prefer “traveler” or “traveller,” understanding the context and conventions of your audience will ensure your writing remains clear, professional, and engaging.